- Non-Structural Column Wraps
- Structural Fiberglass Columns
- Cellular PVC
- Decorative Millwork
- T&G | Shiplap Planks
- Premier Shutters
- Outdoor Living
- Ceiling Beams
- Flexible Mouldings
- Interior Ceilings & Walls
- Wainscoting
- Clearance Items
Glossary of Terms
Glossary of Moulding Related Terms
Crown Moulding
An ornamental moulding runs round the walls of a room at the juncture of walls and ceiling. Also called cornice. Crowns soften the transition from wall to ceiling while adding a distinctive look and charm.
Baseboard
Base moulding is used in decorative architecture to protect the lower portions of walls and covers gaps between wall and floor.
Casing
Casing is the piece of trim that goes around a window or a door, covering the space between the plaster or drywall and the door jamb.
Chair Rail
Chair rail is the piece of moulding that divides the top portion of a wall with the bottom also known as wainscot height.
Wainscot
A lower interior wall surface (usually extending three to four feet up from the floor) contrasts with the wall surface above it. Wainscot can be decorative or protective.
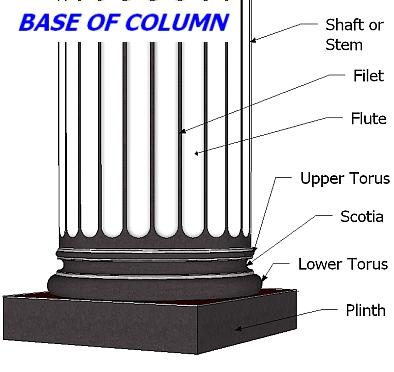
Columns have always played an important role in classical architecture. Each “Architectural Order” or style is distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column used. From the sixteenth century onwards, architectural theorists recognized five orders. Each style has its proper entablature (beam) consisting of an architrave, frieze and a cornice.

Three main parts of a column are the shaft, its base and the capital (top). In classical buildings, the horizontal structure that is supported on the columns like a beam is called an entablature. The entablature is commonly divided into the architrave, the frieze and the cornice. The most common way of distinguishing between the different Classical orders of Architecture is the capital.